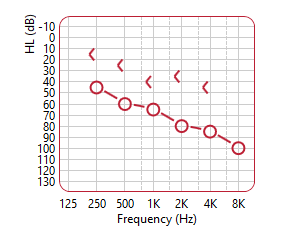
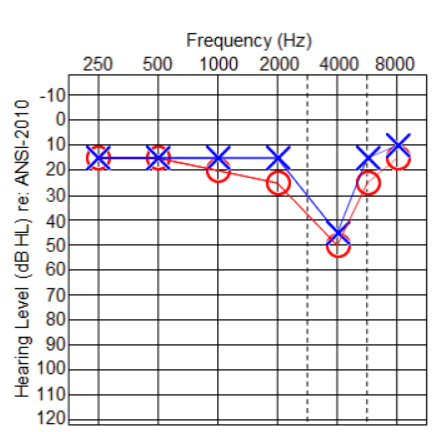
HEARING LOSS

8 SIGNS THAT YOU MAY HAVE HEARING LOSS
Have you noticed anything a bit off during conversations lately? Maybe it feels like people are mumbling more often, or you find yourself feeling exhausted after catching up with friends? Or perhaps your family has been dropping some not-so-subtle hints that you’re missing parts of what they’re saying? It’s often our loved ones who pick up on hearing loss before we do.
But don’t worry—there are some early signs you can watch out for to catch hearing loss in its early stages. Here are eight signs to keep an eye on, because addressing the issue early could help prevent it from getting worse down the road.
1. Your family complains about the TV volume
You may have begun to notice that your family repeatedly asks you to turn the volume down, or that television dialogues are difficult to understand when there is any kind of background music.

2. You can “Hear” but not “Understand”
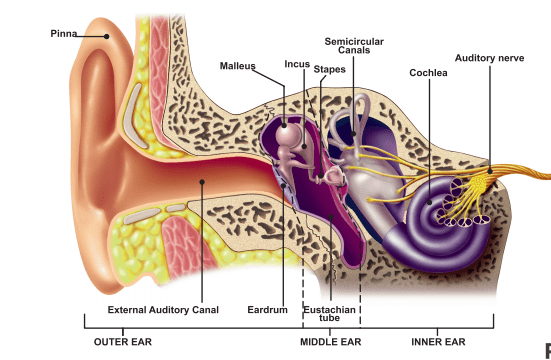
Sometimes, you may not understand what is being said to you even if it is repeated loudly several times. Difficulty understanding speech is one of the first signs of sensorineural hearing loss. Humans hear a wide range of frequencies, and hearing loss may affect some while leaving others intact. A good Digital hearing aid will help differentially amplify only the sounds (frequencies) that are affected.
3. It’s more difficult to hear in noisy situations
Maybe you are talking to your relatives at a wedding, or to your family at a restaurant, or even to the cashier at your grocery store, and you find that you cannot pick out what they are saying from the background noise.
4. You have difficulty understanding speech in groups
Do you find that you cannot follow when several people are talking at once or when you are in a group, often resulting in you feeling left out of the conversation?
5. It’s harder to understand if you can’t see the person’s face
Is it more difficult for you to understand people if they are turned away from you, or if their mouths are covered (with masks)? You may have been reading lip movements to aid your speech understanding.

6. Phone-calls are more difficult than speaking face to face
Difficulty understanding phone conversations even at the highest volumes, could be a sign of hearing loss, as compensating by lip reading is not possible here.
7. You often misunderstand what is said
It can be a humiliating experience to provide the wrong answer to a question. Hearing loss can lead to you missing out some sounds like “s,” “sh,” “tch,” in words, especially in the early stages.

8. You are drained after a conversation
When one of our senses is impaired, all the other senses have to work twice as hard to compensate, and this can be extremely taxing on your brain, leaving you with less energy for things that you want to do or for spending time with your family.
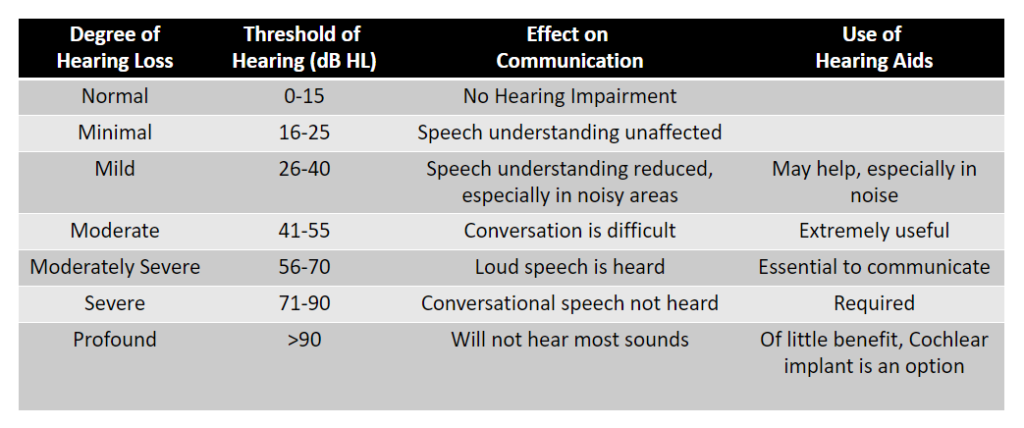
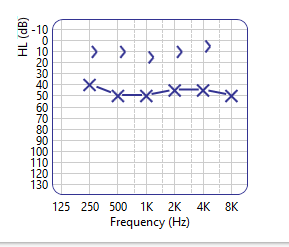
Some amount of difficulty in conversation is normal and experienced even by those who have no hearing loss. But if you notice that these signs are getting more and more frequent, and that you didn’t have these difficulties before, it may be time for you to get a hearing evaluation. Even more so if you fall in the category of those at risk of hearing loss.
Early intervention is key to minimizing further deterioration in hearing. Leaving hearing loss untreated poses several threats such as cognitive decline in older individuals, and withdrawal from society. Hearing science has progressed very far and there are hearing aids that can cater to every budget and every need. Book an appointment with Hearing Point at the earliest for an evaluation and find the perfect solution to your hearing needs.
CONTACT NOW